Credit Card Defaults Part 2: Imbalanced Data and Deployment
Compare Imbalanced Data Approaches, Feature Engineering and Deployment
Summary
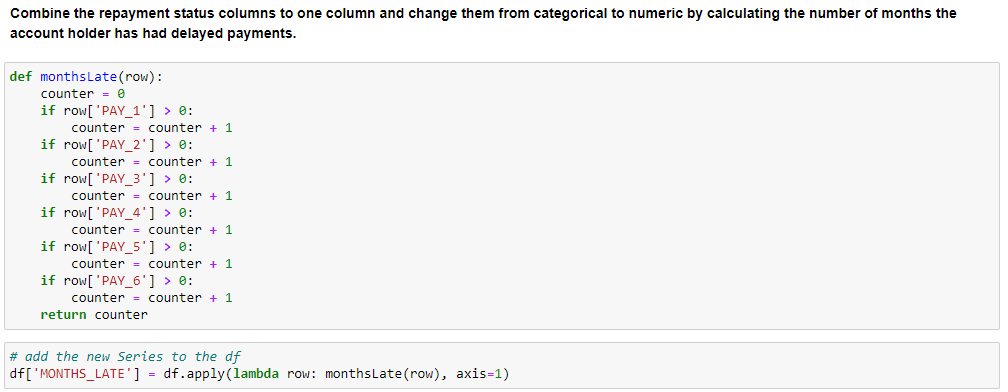
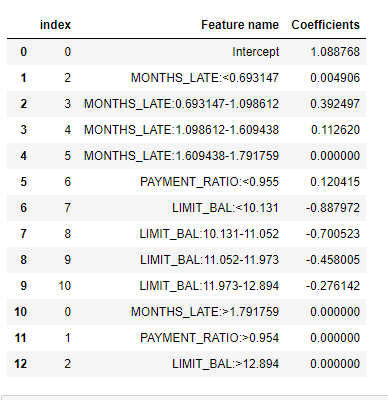
This project includes adjustments and extentions to the a prior credit card defaults project located here. Phase 1 of the credit card default project involved testing five binary classification models for predicting credit card defaults. This Phase 2 of the credit card defaults project includes (1) testing multiple approaches to addressing an imbalanced target variable in a binary classification model, (2) employing methodologies other than Principal Component Analysis to address multicollinearity and feature selection in an effort to be able to analyze individual factors that are significant for defaults, and (3) implementing deployment models to make actual predictions and convert the logistic regression coefficients to a risk score that can be used in making lending decisions.
Tools
- Scikit-learn
- imblearn
- Seaborn
- Matplotlib
- Numpy
- Pandas
- Scipy
Data
Models / Methods / Metrics
- Logistic Regression
- Receiver Operating Characteristic curve and Youden’s J statistic for selecting classification threshold
- Resampling data to address imbalanced target
- Predictions
- Risk score
- Weight of Evidence and Information Value
- Recall
Results
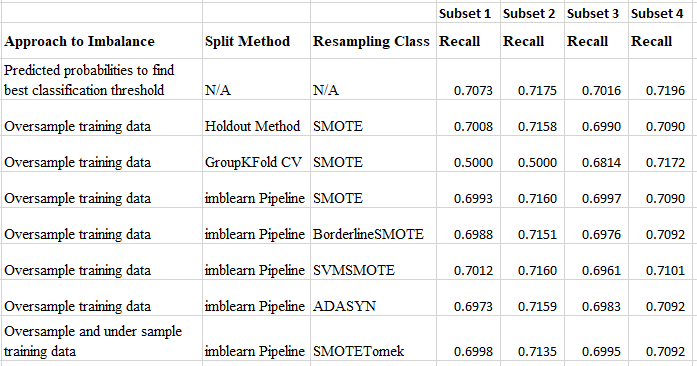
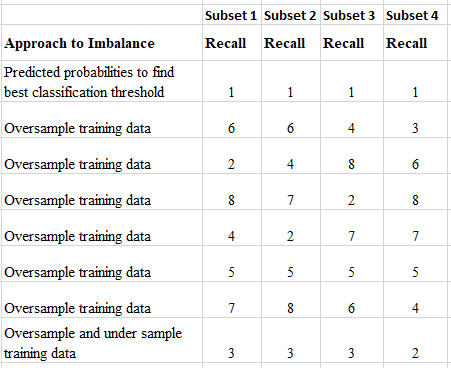
Adjusting the probability classification threshold (without resampling the data) showed the best results for predicting pending defaults. Feature engineering resulted in improved model metrics. Two deployment tools were implemented: (1) predictions of default and (2) a risk score for each account holder.